For illustration purposes, let’s keep our moving average unit cost at $73.13. But if we compute for COGS, let’s extend to five decimal places to minimize rounding differences. When we record a sale, we use the new average unit cost to compute the COGS. In our ledger below, we multiplied 250 units by the new average unit cost of $30. In our books, we record the purchases directly to Merchandise Inventory since we’re using the perpetual inventory system.
Average Cost Method of Inventory Valuation
Finally, standard costing will provide a focus on cost control and overall planning for any organization, and usage is heavily concentrated on large manufacturing organizations. All four of the listed methodologies offer distinct benefits, making it important for management to assess which option aligns best with the strategic direction of their company. The Average Costing Method is a valuable tool for businesses seeking a simple and consistent approach to inventory valuation. Averaging costs provides a stable basis for financial reporting and helps manage price fluctuations.
- The idea is to make the information relating to your choices, especially with strategies.
- It implies at the buying cost of the first item is the cost of the first item sold.
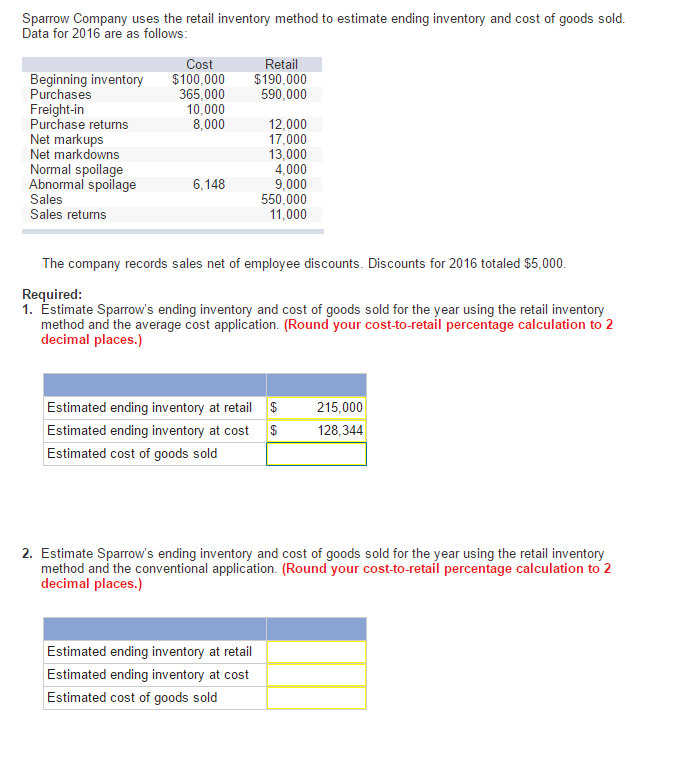
- In a periodic inventory system, all inventory purchases are initially recorded in the Purchases account, which substitutes for the COGS expense during the period.
- Confusion may arise if work-in-process inventory costs incurred by the manufactured items yet to be completed are processed together with the material costs.
- The periodic average cost method does not consider the timing difference of purchases and issues during a period, which is why its value is slightly different from the perpetual method.
Profit Calculation: Key Factors and Their Impact
You’ll see that the actual price at this time is $170 and yet the average cost is only $90. We still have to pay $170 per unit to suppliers even though our costing is at $90. When market prices rise, the average cost is lower than the actual price. This difference has several implications—lower average turbotax 2014 desktop now available cost would mean lower cost of goods sold, higher net income, and higher income taxes. However, a low average cost would not affect the amount that we’ll pay to suppliers. Dividing the total cost with the 25 units of inventory available on that day (5 + 20), the average cost of 1 unit should equal $37.
Advantages & Disadvantages of the AVCO Method
This simplicity can be especially valuable for businesses with extensive inventories that would otherwise require complex tracking of individual item costs. By using the average cost, the administrative burden is lessened, freeing up resources to focus on other areas of the business, such as sales, customer service, or product development. It is particularly beneficial for companies that face volatile purchase prices, as it mitigates the impact of cost variances and provides a stable view of inventory valuation over time. The average cost method is a key approach in inventory valuation, affecting how businesses report their financial health. This method distributes the total cost of goods available for sale evenly across all units, providing a straightforward way to assess inventory value.
Hire An Accountant At The Most Affordable Prices
The accounting information will help you make decisions, especially with your business’s performance or the company you are working for. Understanding its impact is important as it affects areas such as profitability, tax obligations, and cash flow management. By exploring this method, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own.
Now you know what the average cost method is, as well as the advantages and disadvantages it can bring your business from an inventory management perspective. To calculate average cost, take the cost of goods available for sale and divide it by the total number of items from the beginning inventory and purchases. The average cost is not the best cost basis method—as there is really no best method. However, AVCO is the simplest and will usually generate the most stable unit cost of goods sold. That’s why the manual perpetual system can be tedious because of constant averaging.
The last in first out method involves the cost of the previous item purchased becomes the price for the first item to be sold. The cost of the last item you are buying should be the cost of the first item you sell. This culminates in the closure of inventory reported on the balance sheet as the cost of the earliest item that you purchased. In an inflammatory environment, the LIFO method results in ending inventory that is less than the prevailing cost. It means you are selling products to your customers, and as such, you must deal with an inventory.
This approach is advantageous for businesses operating in dynamic markets, such as fashion or consumer electronics, where rapid product turnover is common. The average cost method can have implications for a company’s taxation and cash flow management strategies. By averaging out the cost of goods, this method can lead to more stable taxable income over time. This steadiness can simplify tax planning, as businesses are less likely to experience sharp fluctuations in taxable income that might occur with other valuation methods. When evaluating inventory valuation methods, it’s important to understand how the average cost method compares to alternatives like First-In, First-Out (FIFO) and Last-In, First-Out (LIFO).
